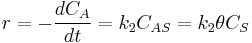Reactions on surfaces
By reactions on surfaces it is understood reactions in which at least one of the steps of the reaction mechanism is the adsorption of one or more reactants. The mechanisms for these reactions, and the rate equations are of extreme importance for heterogeneous catalysis.
Contents |
Simple decomposition
If a reaction occurs through these steps:
A + S ⇌ AS → Products
Where A is the reactant and S is an adsorption site on the surface. If the rate constants for the adsorption, desorption and reaction are k1, k-1 and k2 , then the global reaction rate is:
where 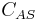 is the concentration of occupied sites,
is the concentration of occupied sites, 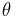 is the surface coverage and
is the surface coverage and 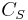 is the total number of sites (occupied or not).
is the total number of sites (occupied or not).
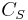 is highly related to the total surface area of the adsorbent: the greater the surface area, the more sites and the faster the reaction. This is the reason why heterogeneous catalysts are usually chosen to have great surface areas (in the order of a hundred m2/gram)
is highly related to the total surface area of the adsorbent: the greater the surface area, the more sites and the faster the reaction. This is the reason why heterogeneous catalysts are usually chosen to have great surface areas (in the order of a hundred m2/gram)
If we apply the steady state approximation to AS, then:
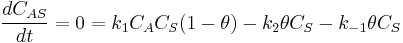 so
so 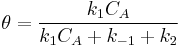 and
and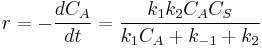 .
.
Note that, with 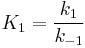 , the formula was divided by
, the formula was divided by 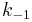 .
.
The result is completely equivalent to the Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The rate equation is complex, and the reaction order is not clear. In experimental work, usually two extreme cases are looked for in order to prove the mechanism. In them, the rate-determining step can be:
- Limiting step: Adsorption/Desorption
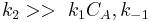 , so
, so 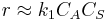 .
.
The order respect to A is 1. Examples of this mechanism are N2O on gold and HI on platinum
- Limiting Step: Reaction
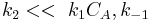 so
so 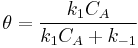
which is just Langmuir isotherm and 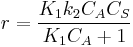 .
.
Depending on the concentration of the reactant the rate changes:
-
- Low concentrations, then
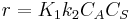 , that is to say a first order reaction in component A.
, that is to say a first order reaction in component A. - High concentration, then
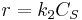 . It is a zeroth order reaction in component A.
. It is a zeroth order reaction in component A.
- Low concentrations, then
Bimolecular reaction
Langmuir-Hinshelwood mechanism
Langmuir-Heishelwood-Hougen-Watson This mechanism proposes that both molecules adsorb and the adsorbed molecules undergo a bimolecular reaction:
A + S ⇌ AS
B + S ⇌ BS
AS + BS → Products
The rate constants are now 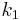 ,
,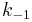 ,
,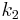 ,
,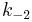 and
and 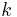 for adsorption/desorption of A, adsorption/desorption of B, and reaction. The rate law is:
for adsorption/desorption of A, adsorption/desorption of B, and reaction. The rate law is: 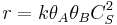
Proceeding as before we get 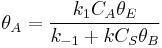 , where
, where 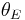 is the fraction of empty sites, so
is the fraction of empty sites, so 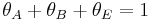 . Let us assume now that the rate limiting step is the reaction of the adsorbed molecules, which is easily understood: the probability of two adsorbed molecules colliding is low. Then
. Let us assume now that the rate limiting step is the reaction of the adsorbed molecules, which is easily understood: the probability of two adsorbed molecules colliding is low. Then 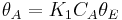 , with
, with 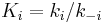 , which is nothing but Langmuir isotherm for two adsorbed gases, with adsorption constants
, which is nothing but Langmuir isotherm for two adsorbed gases, with adsorption constants 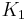 and
and 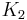 . Calculating
. Calculating 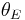 from
from 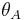 and
and 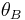 we finally get
we finally get
-
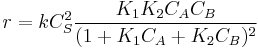 .
.
The rate law is complex and there is no clear order respect to any of the reactants but we can consider different values of the constants, for which it is easy to measure integer orders:
- Both molecules have low adsorption
That means that 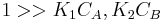 , so
, so 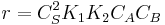 . The order is one respect to both the reactants
. The order is one respect to both the reactants
- One molecule has very low adsorption
In this case 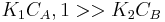 , so
, so 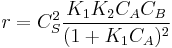 . The reaction order is 1 respect to B. There are two extreme possibilities now:
. The reaction order is 1 respect to B. There are two extreme possibilities now:
-
- At low concentrations of A,
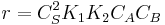 , and the order is one respect to A.
, and the order is one respect to A. - At high concentrations,
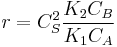 . The order is minus one respect to A. The higher the concentration of A, the slower the reaction goes, in this case we say that A inhibits the reaction.
. The order is minus one respect to A. The higher the concentration of A, the slower the reaction goes, in this case we say that A inhibits the reaction.
- At low concentrations of A,
- One molecule has very high adsorption
One of the reactants has very high adsorption and the other one doesn't adsorb strongly.
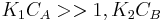 , so
, so 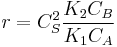 . The reaction order is 1 respect to B and -1 respect to A. Reactant A inhibits the reaction at all concentrations.
. The reaction order is 1 respect to B and -1 respect to A. Reactant A inhibits the reaction at all concentrations.
The following reactions follow a Langmuir-Hinshelwood mechanism [1]:
- 2 CO + O2 → 2 CO2 on a platinum catalyst.
- CO + 2H2 → CH3OH on a ZnO catalyst.
- C2H4 + H2 → C2H6 on a copper catalyst.
- N2O + H2 → N2 + H2O on a platinum catalyst.
- C2H4 + ½ O2 → CH3CHO on a palladium catalyst.
- CO + OH → CO2 + H+ + e- on a platinum catalyst.
Eley-Rideal mechanism
In this mechanism, proposed in 1938 by D. D. Eley and E. K. Rideal, only one of the molecules adsorbs and the other one reacts with it directly from the gas phase, without adsorbing:
A(g) + S(s) ⇌ AS(s)
AS(s) + B(g) → Products
Constants are 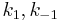 and
and  and rate equation is
and rate equation is 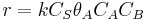 . Applying steady state approximation to AS and proceeding as before (considering the reaction the limiting step once more) we get
. Applying steady state approximation to AS and proceeding as before (considering the reaction the limiting step once more) we get 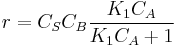 . The order is one respect to B. There are two possibilities, depending on the concentration of reactant A:
. The order is one respect to B. There are two possibilities, depending on the concentration of reactant A:
-
- At low concentrations of A,
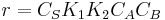 , and the order is one with respect to A.
, and the order is one with respect to A.
- At low concentrations of A,
-
- At high concentrations of A,
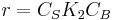 , and the order is zero with respect to A.
, and the order is zero with respect to A.
- At high concentrations of A,
The following reactions follow a Eley-Rideal mechanism [2]:
- C2H4 + ½ O2 (adsorbed) → H2COCH2 The dissociative adsorption of oxygen is also possible, which leads to secondary products carbon dioxide and water.
- CO2 + H2(ads.) → H2O + CO
- 2NH3 + 1½ O2 (ads.) → N2 + 3H2O on a platinum catalyst
- C2H2 + H2 (ads.) → C2H4 on nickel or iron catalysts
See also
References
Graphic models of Eley Rideal and Langmuir Hinshelwood mechanisms
German page with mechanisms, rate equation graphics and references